Mere numbers may not be the easiest way to gauge the health of Sri Lanka’s labor market. However, recent data released by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka show changes in labor force participation, falling below 50 percent of the total employable population.
Words Jennifer Paldano Goonewardane.
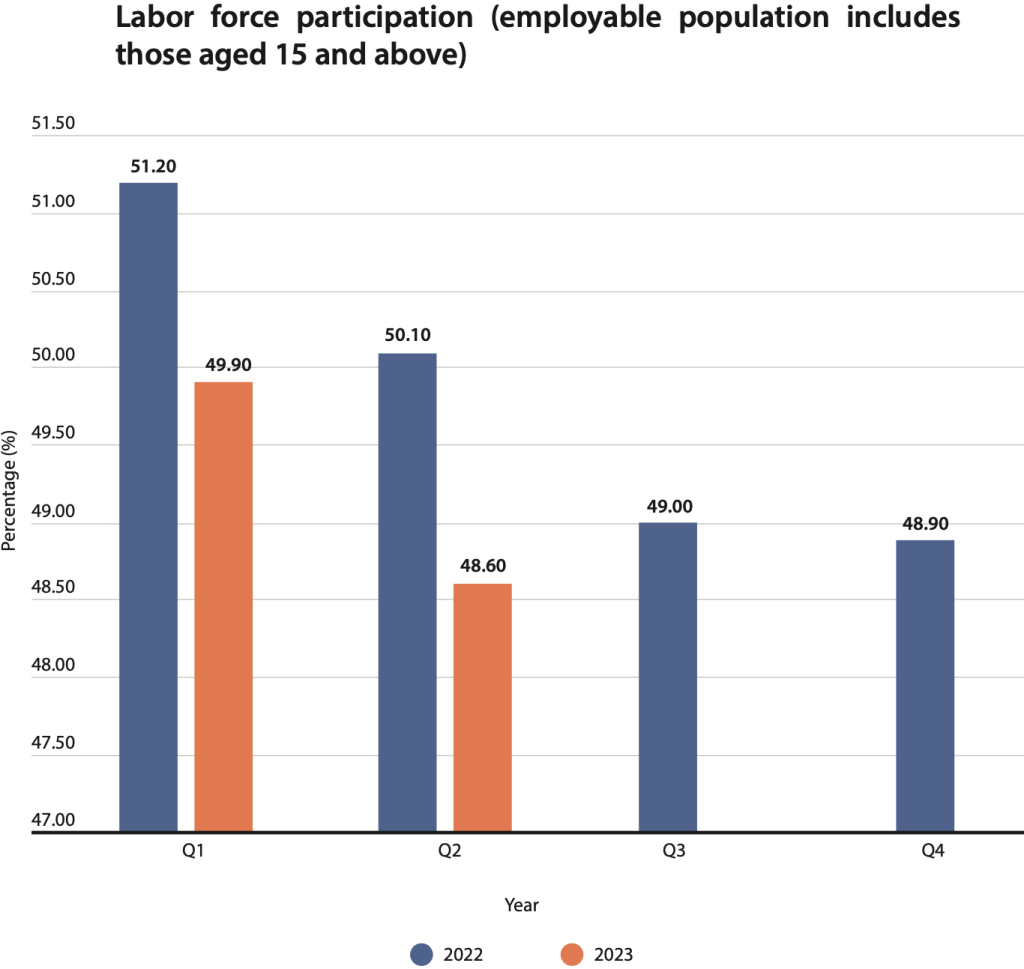
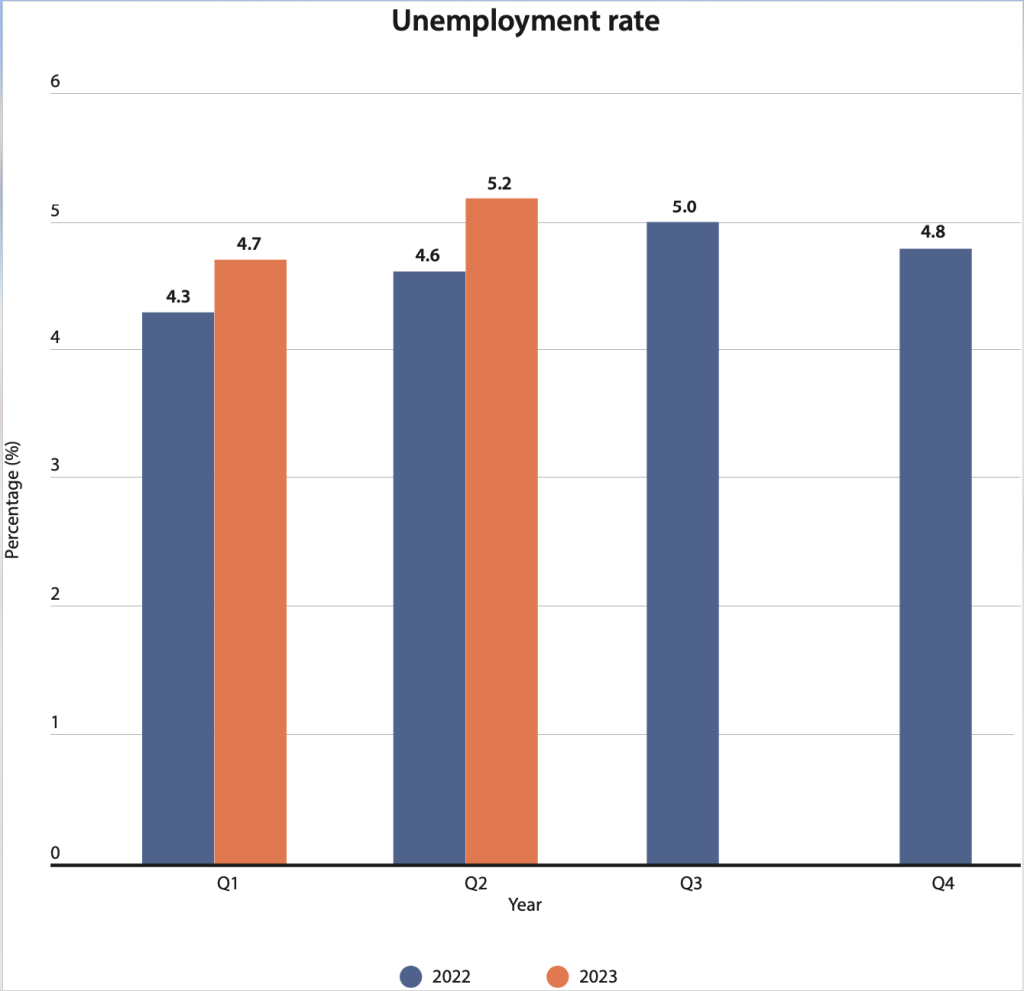
In an estimated eight million employed persons in Sri Lanka, according to data, labor force participation (employable population includes those aged 15 and above) in the first quarter of 2023 was 49.9 percent. The unemployment rate in the first quarter of 2023 was 4.7 percent. In the second quarter of 2023, labor force par ticipation was 48.6 while unemployment stood at 5.2. Between the first two quarters of 2023, there has been a 2.6 percent reduction in the country’s labor force participation. In the first quarter of 2023, employment by economic activity stood at 26.7 percent for agriculture, 25.5 percent for industry, and 47.8 percent for services. This data for the second quarter of 2023 stood at 25.7 percent for agriculture, 26.3 percent for industry, and 48.1 for services, recording a one percent decline in agriculture sector jobs but a marginal 0.8 percent increase in manufacturing sector employment and a 0.3 percent increase in services sector jobs. Declining jobs in the manufacturing sector, evident in 2022, show an increasing trend in the first two quarters of 2023. However, jobs in the agriculture sector, which had picked up towards the latter part of 2022, show declines in the first and second quarters of 2023. Jobs in the services sector have also picked up in the second quarter of 2023.
In the first quarter of 2022, the labor force participation rate was 51.2 percent, while unemployment was 4.3 percent. Employment in agriculture in the first quarter of 2022 was 25.0 percent, while employment in industry was 27.9 percent, and 47.1 percent was in services. Labor force participation in the second quarter of 2022 was 50.1 percent, while the unemployment rate was 4.6 percent, a 0.3 percent increase from the previous quarter. Labor force participation in agriculture in the second quarter of 2022 was 26.0 percent, a one percent increase from the last period, 27.7 percent labor force participation in industry, a 0.2 percent decline in the second quarter, while services sector participation also recorded a 0.8 percent decline to 46.3 percent. Third quarter 2022 data indicate 49.0 percent labor force participation, a drop of 1.1 percent compared to the second quarter, while unemployment rose by 0.4 percent to five percent from the previous quarter, with participation spread across agriculture, industry, and services recording 26.9 percent, 0.9 percent improvement in agriculture sector jobs of the prior quarter. However, the industrial sector labor force participation continued its downward trend with a 1.8 percent decline from the previous quarter to 25.9 percent.
Meanwhile, the services sector employment participation increased by 0.9 percent in the third quarter to record 47.2 percent, respectively. A slight decline in labor force participation in the fourth quarter of 2022, stood at 48.9 percent, but unemployment declined by 0.2 percent to 4.8 percent. Employment in agriculture had risen to 28.2 percent in the fourth quarter of 2022, an improvement of 1.3 percent from the previous quarter, while jobs in manufacturing stood at 24.3 percent, a 1.6 percent decline in comparison to the last quarter, while the services sector recorded a marginal increase at 47.5 percent.
As 2022 ended with a labor force participation of 48.9 percent, the first quarter of 2023 recorded a one percent improvement at 49.9 percent, while unemployment declined by 0.1 percent in the first quarter of 2023 as opposed to the fourth quarter of 2022. A comparison of labor force participation according to sectors between the last quarter of 2022 and the first quarter of 2023 also provides mixed performances. While employment in agriculture in the fourth quarter of 2022 was 28.2 percent, it declined to 26.7 percent in the first quarter of 2023, a 1.5 percent decline in the new period. Jobs in the industrial sector in the fourth quarter of 2022 were 24.3 percent, improving by 1.2 percent in the first quarter of 2023 to 25.5 percent. Likewise, employment participation in the services sector stood at 47.5 percent in the fourth quarter of 2022, which was 47.8 in the first quarter of 2023, an improvement of 0.3 percent. Jobs in the agriculture sector picked up in the fourth quarter of 2022, a 1.3 percent increase from the third quarter.
Labor force participation in the first quarter of 2021 was 50.9 percent, and the unemployment rate was 5.7 percent.
The only available employment data from the Central Bank of Sri Lanka for 2023 pertains to only the first two quarters when unemployment surpassed five percent in the 2Q of 2023.
Sector-level employment figures for the first quarter of 2021 were not available. Employment in the second quarter of 2021 was 49.8 percent, and the unemployment rate was 5.1 percent. Labor force participation across agriculture, industry, and services stood at 27.8 percent, 25.3 percent, and 46.9 percent. In the third quarter of 2021, labor force participation stood at 49.5 percent, and unemployment at 5.2 percent. In the third quarter of 2021, jobs in agriculture stood at 29.7 percent, industry at 24.5 percent, and services at 45.8 percent. The fourth quarter of 2021 recorded 49.5 percent labor force participation with an unemployment rate of 4.6 percent, where jobs in the agriculture sector were 26.1 percent, industry 27.0 percent, and services 46.9 percent. In the first quarter of 2021, the unemployment rate remained above five percent until declining below five percent in the fourth quarter, a trend that continued into the first two quarters of 2022, reaching five percent in the third quarter and falling again in the fourth quarter of 2022.
The only available employment data from the Central Bank of Sri Lanka for 2023 pertains to only the first two quarters when unemployment surpassed five percent in the second quarter of 2023. Jobs in manufacturing in 2021 declined in the third quarter and eventually picked up by 2.5 percent to 27.0 percent in the fourth quarter, continuing the trend in the first two quarters of 2022. The decline in manufacturing sector jobs beginning with the third quarter of 2022 continued into the fourth quarter, recording a 1.6 percent decline compared to the third quarter while picking up in the first and second quarters of 2023.
The data could be looked at in the backdrop of the country’s economy, whether the economic downturn impacted labor force participation and drove people to seek employment abroad for higher wages, which in turn may have affected businesses in sourcing adequate talent/skilled personnel to fill positions in the various sectors.