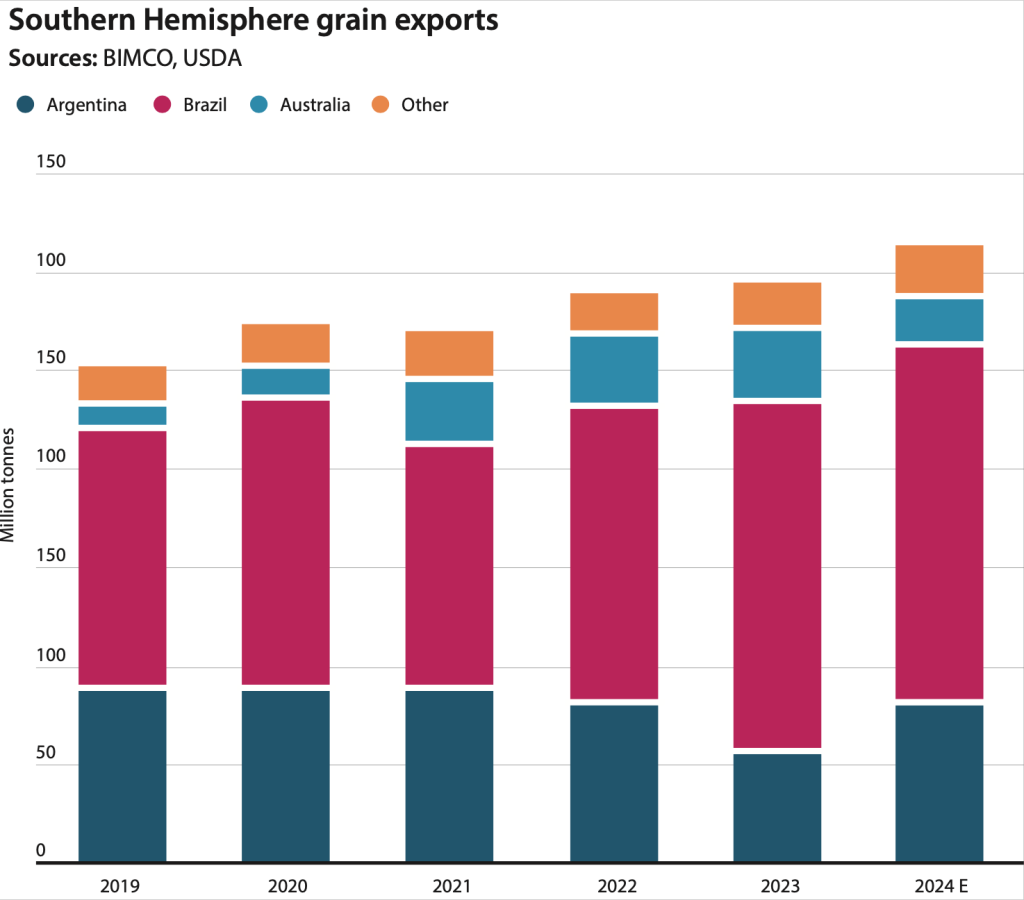
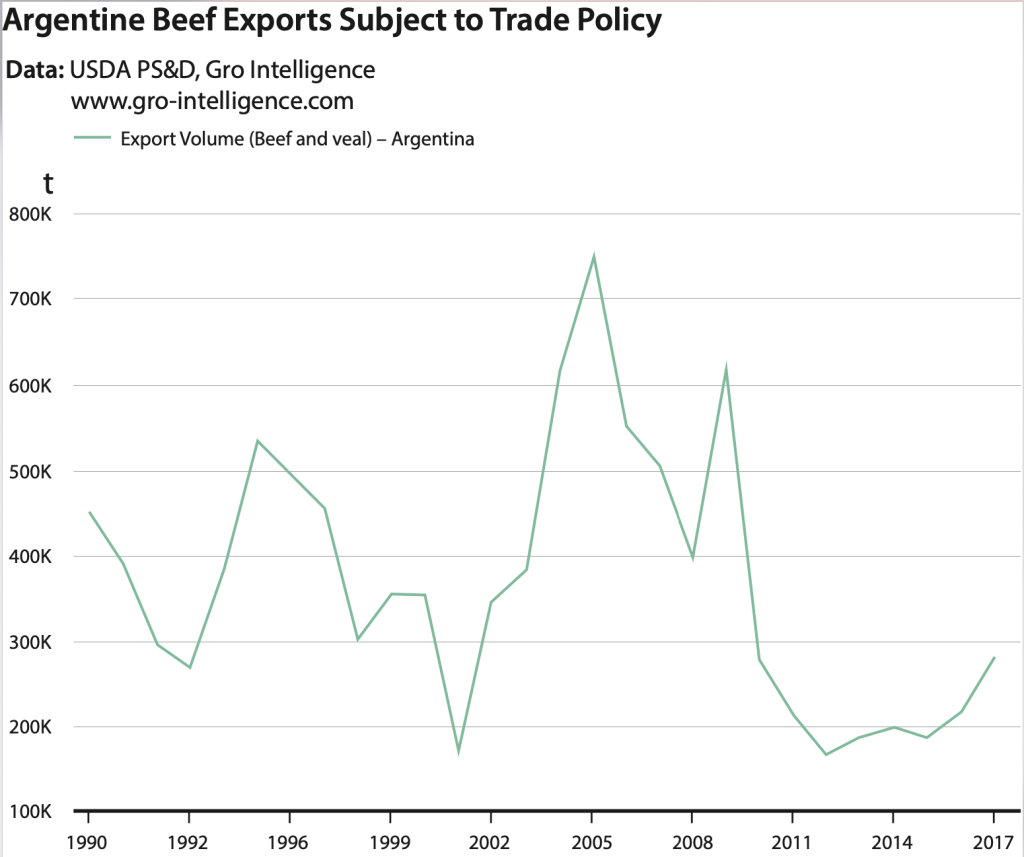
In October 2024, Argentina recorded a remarkable trade surplus of USD 888 million, marking a significant recovery from the USD 442 million trade deficit in October 2023. This shift in trade dynamics underscores Argentina’s economic resilience and the effectiveness of recent policy measures aimed at bolstering exports and managing imports.

Drivers of Export Growth
Exports soared by 30 percent year-on-year, reaching USD 6,934 million. This growth was driven by robust performance in key sectors:
Agriculture: Agricultural exports surged by 47.8 percent, showcasing Argentina’s strength as a global supplier of grains, oilseeds, and other raw materials. Favorable weather conditions and increased global demand played a crucial role.
Manufactured Goods: Exports of manufactured products grew by 27 percent, reflecting improved industrial productivity and competitiveness in international markets.
Energy and Fuels: A 33.5 percent increase in the export of fuels and energy highlighted the growing importance of the energy sector in Argentina’s trade portfolio.
Controlled Import Growth
Imports grew modestly by 4.9 percent, reaching USD 5,954 million. This controlled growth reflects both the government’s strategic import management and reduced domestic demand due to tighter economic conditions. Key changes in import categories included:
A significant decline in capital goods (-37.6 percent) and accessories for capital goods (-31 percent), suggesting businesses are scaling back investments in machinery and equipment.
A slight decrease in intermediate goods (-2.5 percent), which are essential for production processes.
Economic and Policy Context
Argentina’s improved trade performance is supported by a combination of external factors and domestic policy initiatives:
Government Policies: The fiscal stabilization program, which emphasizes fiscal discipline and a “zero monetary issuance” policy, has bolstered investor confidence and reduced inflationary pressures. These measures have improved the competitiveness of Argentine exports.
Currency Management: The government has maintained a stable exchange rate, helping exporters benefit from favorable currency conditions without significant volatility.
Global Demand: Rising global demand for commodities, particularly in the agriculture and energy sectors, has provided a strong tailwind for export growth.
Broader Economic Impact
The trade surplus is part of a broader economic recovery for Argentina. Between January and September 2024, the country achieved a fiscal surplus for the first time in years, marking a turning point in its economic trajectory. Key indicators of this recovery include:
Reduced Country Risk: Argentina’s country risk has fallen from 2,100 points in January 2024 to 1,280 in October, reflecting increased investor confidence.
Inflation Control: Although inflation remains a challenge, it has shown signs of moderation, supporting domestic economic stability.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, Argentina’s trade prospects appear optimistic:
Energy Sector Growth: The development of the Vaca Muerta shale formation and other energy projects is expected to significantly boost exports in the coming years.
Projected Trade Surplus: The Central Bank forecasts a trade surplus of USD 22.4 billion for 2024, with potential to reach USD 41.8 billion by 2030, driven by sustained export growth and disciplined import management.
Diversification: Continued efforts to diversify export markets and products will help Argentina reduce its vulnerability to external shocks.
Challenges and Risks
While the recent trade performance is encouraging, challenges remain. High inflation, limited access to international credit markets, and political uncertainty could pose risks to sustained economic recovery. Additionally, the country must address structural issues, such as infrastructure gaps and regulatory inefficiencies, to maintain its competitive edge.
Argentina’s USD 888 million trade surplus in October 2024 marks a significant turnaround from the previous year’s deficit. With exports surging and imports under control, the country is on a path to economic stabilization and growth. Continued policy discipline, combined with favorable global conditions, will be crucial for sustaining this positive momentum in the years ahead.