ECONOMY IN BRIEF
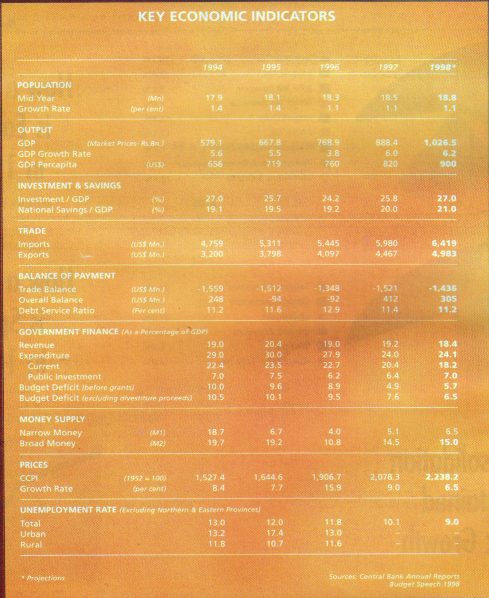
■ Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is set to exceed 6 per cent growth in 1997 with signs for further acceleration next year.
■ The rate of inflation declined from 20 per cent in October last year to 7 per cent in October this year. Average inflation for the year is estimated to decline to 9 per cent from 16 per cent in 1996.
■ Interest rates declined with yield on one year Treasury bills falling to 10 per cent in 1997 from 17 percent in 1996 and the prime lending rate declining to 12 per cent from 18 per cent.
■ Unemployment declined to around 10 per cent of the labour force.
■ Investment reached 26 per cent of GDP and National Savings 21 per cent.
■ Exports increased by 14 per cent, overseas remittances by 9 per cent and long term foreign aid by 27 per cent. Current ac- count deficit declined to 4 per cent of GDP.
■Foreign investments exceed US$ 550 million and inflows of long term foreign capital are on the rise.
■The burden of external debt continues to ease with the debt service ratio falling to 13 per cent and the external debt to GDP declining to 62 per cent.
■ Short term external borrowings remain less than 1 per cent of total capital inflows insuring Sri Lanka’s economy against volatile capital movements.
■ Balance of Payments records a surplus of over US$ 400 million.
■ Gross External Assets at US$ 2.5 billion provides over 5 months import cover.
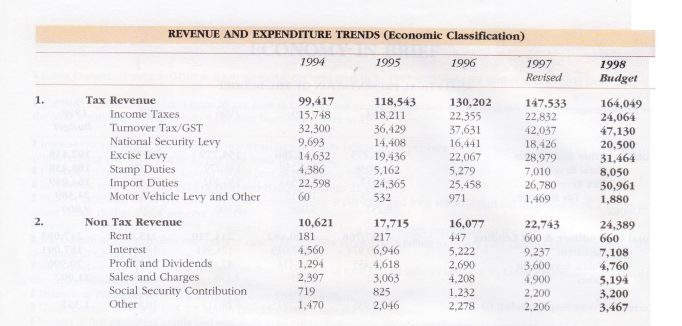
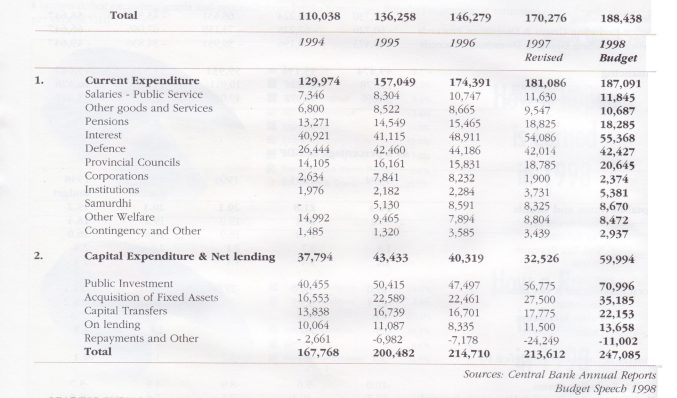
■Budget deficit excluding grants and proceeds from Public Enterprises Reform Programme is estimated to decline to about 7.6 per cent of GDP.

PEOPLE’S BUDGET FOR A STABLE ECONOMY TO THE 21ST CENTURY OBJECTIVES
1.Achieve rapid development in following priority sectors:
■Research and Development
■ Agriculture
■Tourism
■Gold, Gem and Jewellery
■ Textiles Through outright grants and concessional credit, lower taxation, investment tax allowance for increased investments, duty free import of material, equipment, accessories, machinery and other concessions.
2. Accelerate investments on thrust industries through BOI incentives and infrastructure facilities:
■Electronics and computer assembly
■Ceramic and glassware manufacture
■Rubber based industries
■Light and heavy engineering industries
■Cutting and polishing of gems, diamonds and manufacture of jewelry
3. Promote regional industrialization through BOI incentives and the development of industrial infrastructure and guaranteed quotas and other facilities:
■Industrial relocation
■Establishment of dedicated economic centres
■Establishment of 50 new garment factories in the South and selected districts in other provinces.
4. Liberalise textiles, gem, gold and jewellery industries.
5. Reduce the overall cost of production and improve productivity through the removal of customs duty on basic raw materials and intermediate inputs such as fertilizer, agrochemical, seed processing equipment and machinery, tea packaging machinery, agricultural tractors, lorries, refrigerator trucks, spare parts for fishing boats, fish finding devices, rattan and bamboo, computers and communication equipment, medical and dental equipment and accessories, fabrics, yarn, equipment and consumable items, handloom material and equipment.
6. Encourage young entrepreneur development through venture capital companies – Ruhunu 2001 through concessional lending.
7. Expand capital market through increased listing of companies in the stock market – tax bonus, lower stamp duties, tax deduction for expenses in respect of listing, investment tax allowance for share purchases, the establishment of a settlement guarantee fund, removal of capital gains from income tax for purposes of listing and release of funds from NSB, ETF, EPF and insurance for investments in stock market, incentives for unit trusts and relaxation of direct foreign investment entry.
8. Deepen debt market through the reduction of stamp duties on financial instruments, incentives for private debt instruments and reduction in turnover tax on banking and financial institutions from 2 per cent to 1 percent.
9. Promote Special Development Programs
■President’s Fund for Innovators
■Two tier private hospitals
■Low cost housing complexes
■Development of software industry
■Incentives for worker transport through the release of long term funds, tax concessions and housing loan schemes.
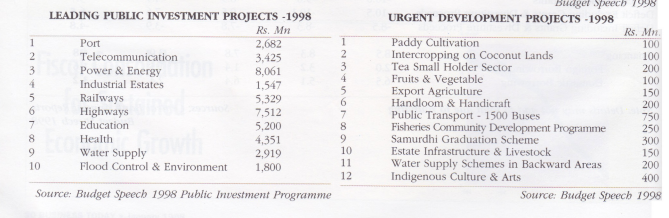
10. Provide enhanced public investments for development of: equipment
■Public bus and rail transport
■Fisheries community housing program and infrastructure facilities
■Samurdhi graduation through leasing facilities to provide three wheelers, two wheel tractors etc.
■Promotion of handlooms and handicrafts through soft loans and duty free imports of raw material, accessories,
■Basic estate infrastructure development through community projects
■Water supply schemes in backward areas
■Indigenous culture and arts – 25 cultural centres; Jaffna Library and National Cultural Complex.
11. Provide relief to public servants
■Reduction of interest on loans to 4.2 per cent
■60 per cent salary revision to those below Rs.7,500 from January 1, 1998 and for others from July 1, 1998
■5 per cent increase to pensioners
■ Performance incentives res
12. Improve expenditure controls and management
■ 10 per cent cut on selected expenditure items other than those on salaries, pensions and household transfers ex- cept on education and health
■Public corporations, state banks. statutory agencies to conform to 10 cent cut in expenditure
■Borrowing limits on public enterprises to be strictly enforced
■Additional levies on profit making public enterprises
13. Reduce Treasury bill borrowing limit from Rs.125,000 million to Rs.115,000 million and redeem Government bonds issued to state banks.
14. Rationalisation of Government revenue:
■Retirement benefits under voluntary retirement schemes to be free from income tax
■Simplification of Advance Company Tax (ACT)
■The reduction in income tax from 35 per cent to 15 per cent on agriculture, fisheries, livestock and tourism
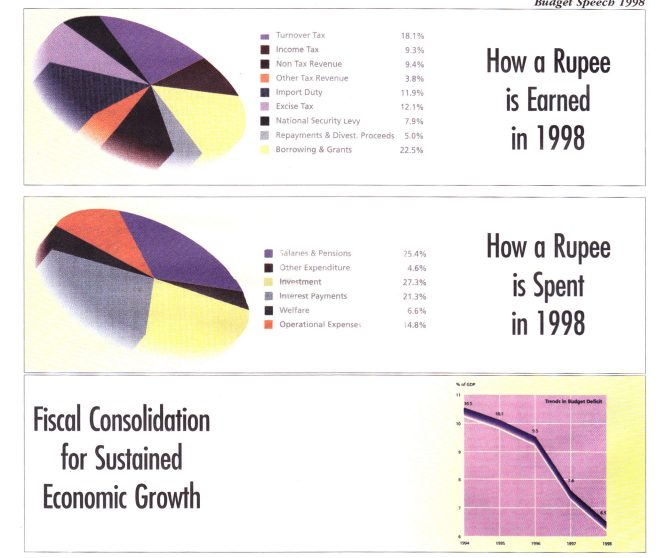
■Turnover tax rates of 7, 11 and 20 replaced with 8, 12 and 18 with a lower mark-up of 10 per cent on imports and replaced with Goods and Services Tax (GST) from April 1, 1998 at 12.5 per cent
■Medical charges, local dairy products exempt from turnover tax
■Turnover tax on banking and financial institutions to continue at 1 per cent
■National Security Levy and Save the Nation Contribution to be continued.
■Excise taxation confined to revenue items with adjustments in tax rates on cigarettes, liquor and selected motor vehicles to off set revenue loss from turnover tax.
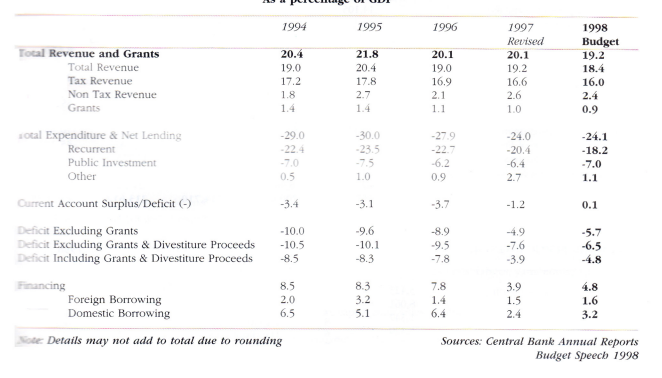
15. Achieve a current account surplus of Rs.1.3 billion (0.1 per cent of GDP) and contain the overall deficit inclusive of grants and divestiture proceeds to Rs.49.6 billion (4.8 per cent of GDP) and exclusive of grants and divestiture proceeds to Rs 66.7 billion (6.5 per cent of GDP).




